China's "Twelfth Five-Year Plan" strongly supports the emerging industries of new energy vehicles based on electric vehicles. However, safety accidents of lithium-ion battery systems characterized by thermal runaway have occurred, which has plagued the development of electric vehicles. What are the common forms and causes of power battery safety accidents? What kind of precautions should I take? Xiaobian takes you to the point.
1 Power battery safety issuesThe lithium-ion battery accident is mainly caused by the fire caused by the thermal runaway. As shown in Table 1 and Figure 1.
Table 1 Lithium-ion battery accidents occurred in recent years

Figure 1 Some lithium ion power battery accidents in recent years
The safety issues of lithium-ion battery systems are manifested in three levels (Figure 2).
1) "Evolution" of battery system security. That is, the long-term aging of the battery system - "evolution" (accident 1, 2, 3, 5, 7) and sudden damage to the battery system - "mutation" (accidents 4, 6).
2) "Trigger" - the turning point of lithium-ion battery from normal operation to thermal runaway and fire.
3) "Extension" - the secondary hazard to the surrounding by thermal runaway.
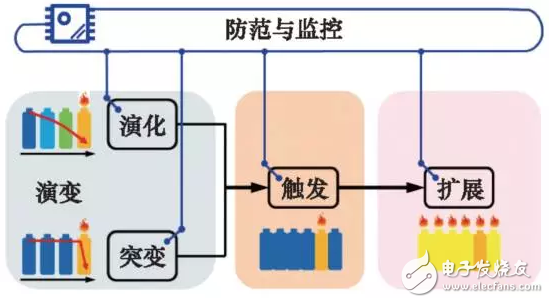
Figure 2 The level of safety issues in the power battery system
2 Evolution of power battery safety 2.1 “evolution†and “mutationâ€The reliability of the long-term aging of the battery system is reduced, and the evolution takes a long time. The battery system can be tested for the safety of the battery system by comparing the aging degree of the battery system. In contrast, the safety mutation is difficult to predict, but can be in the form of an existing accident. To improve the design of the battery system.
2.2 Security evolution mechanismAging of any component of the battery system can trigger a safety incident, such as accidents 1, 7. In addition, the safety evolution of the battery itself is mainly manifested by the development of internal short circuits. The growth of metal dendrites inside the battery is one of the main causes of internal short circuits. It is worth mentioning that the energy density of the aging battery is reduced, and the damage caused by thermal runaway may be reduced; on the other hand, the aging battery is more susceptible to thermal runaway.
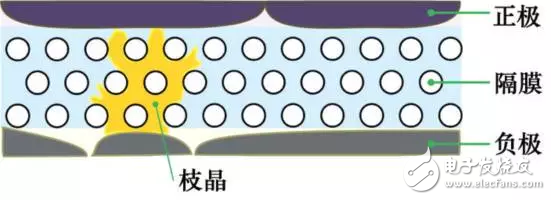
Figure 3: Growth of metal dendrites inside the lithium-ion battery and piercing of the separator
3 Battery safety accident trigger 3.1 Thermal runaway mechanismAfter the evolution process, battery accidents will enter the “trigger†phase. Generally, after this, the energy inside the battery will be released in an instant, causing thermal runaway, causing smoke, fire and explosion. Of course, in a battery safety accident, thermal runaway may not occur. The battery after thermal runaway may not simultaneously emit smoke, fire or explosion, or it may not occur, depending on the mechanism of thermal runaway of the battery material.
Figure 4, Figure 5 and Table 2 show the thermal runaway mechanism of a 25 A·h lithium-ion battery with a ceramic separator/graphite anode with a ternary positive electrode/PE matrix. The thermal runaway process is divided into seven phases.
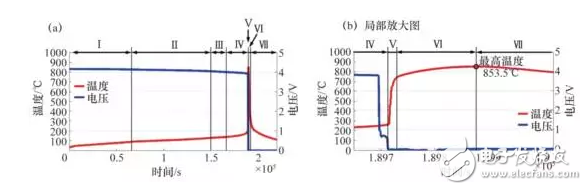
Figure 4 Thermal runaway test data of a ternary lithium-ion power battery (experimental instrument is a large-scale accelerated adiabatic calorimeter, EV-ARC)
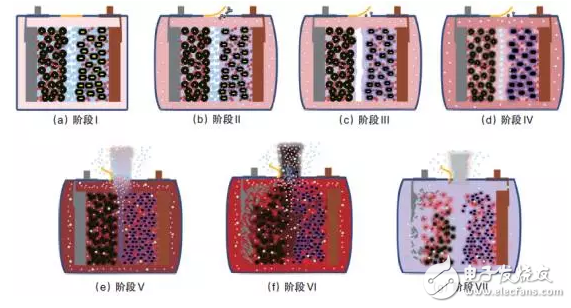
Figure 5 Mechanism of different stages of thermal runaway of a ternary lithium-ion battery
Table 2 Staged characteristics and mechanism of thermal runaway of a lithium-ion battery

In the case of smoking, in stage V, if the internal temperature of the battery is lower than the melting temperature of the positive current collector aluminum foil by 660 ° C, the positive electrode coating of the battery will not be ejected with the gas generated by the reaction, and the observed white will be white. Smoke; otherwise it is black smoke.
In the case of fire, the main cause of ignition is that the temperature of the gas ejected is higher than its flash point, and the electrolyte gas reacts violently with oxygen.
In the case of an explosion, the necessary condition is that the inside of the battery has a high-pressure gas accumulation, and the safety valve is the key to releasing the high-pressure accumulated gas in time.
3.2 Accident triggered classificationAccording to the characteristics of the trigger, it can be divided into three categories: mechanical trigger, electric trigger and hot trigger.
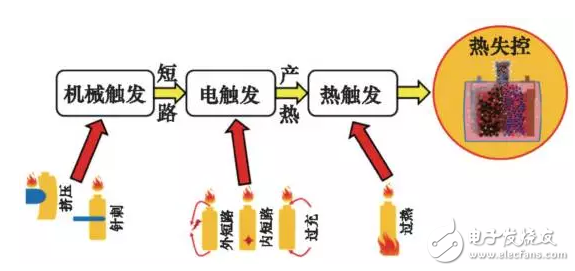
Figure 6 Accident triggered classification
4 Thermal runaway expansion in the battery system 4.1 Hazard of thermal runaway expansionAfter the thermal runaway is triggered, the heat released by the local monomer after the thermal runaway will propagate to the surroundings, which may heat the surrounding battery and cause thermal runaway of the surrounding battery, thereby causing great damage to the chain reaction.
4.2 Mechanism of thermal runaway expansionThere are three possible main paths for heat transfer during thermal runaway expansion: 1) thermal conduction between adjacent battery housings; 2) thermal conduction through the battery poles; 3) firing of the individual cells against the surrounding battery.
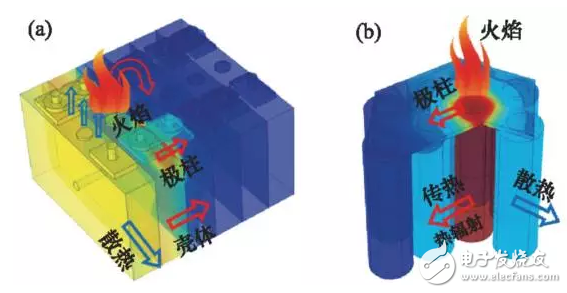
Figure 7 Several possible paths for thermal runaway expansion
4.3 Preventing the conflict between thermal runaway expansion and battery system designMeasures:
1) Prevent the occurrence of flames. Design the spray direction of the valve body to guide the direction of flame formation; add fire extinguishing agent; ensure sealing.
2) Consider the influence of high temperature gas diffusion on other components of the battery system, and discharge high temperature gas in time.
3) Properly block the heat transfer path between the cells, such as providing an insulating layer between the cells.
4) Enhance the heat dissipation inside the battery system; discharge the battery around the faulty battery; fill the phase change material between the batteries to absorb heat and the like to suppress the expansion of the thermal runaway.
contradiction:
There are certain contradictions between the design of preventing thermal runaway expansion and other functional design of the battery system, such as increasing internal temperature unevenness, reducing specific energy, and increasing cost. Coordinating this contradiction is one of the important topics in the design of battery system safety.
5 Battery accident prevention and safety monitoringIn addition to the prevention of thermal runaway expansion, the power battery system requires a full range of accident prevention measures and safety monitoring measures.
1) Lithium-ion power batteries must pass the relevant safety test standards before mass production and sales.
2) Taking the prevention of thermal runaway accidents as the core, the safety design of the power battery system needs to consider factors such as “evolutionâ€, “trigger†and “expansion†of the accident. There is also a clear understanding of the failure modes of the various components.
3) The power battery system needs to be properly managed during operation and monitor and warn about possible accident triggering trends.
6 ConclusionThe safety of power battery systems is mainly divided into three levels, namely “evolutionâ€, “trigger†and “expansionâ€. Starting from these three levels, in-depth study of the mechanisms of each level and its evolution process, and the introduction of effective accident prevention measures and safety monitoring measures are the focus of the next research.
Note: This article is organized from the Science and Technology Herald 2016, 34(6). Edited by the front of the new energy front
MICROBITS TECHNOLOGY LIMITED , https://www.hkmicrobits.com