A wheel accumulator with a large moment of inertia mounted on the machine's rotary shaft. When the machine speed increases, the kinetic energy of the flywheel increases, and the energy is stored. When the machine speed decreases, the kinetic energy of the flywheel is reduced, and the energy is released. Flywheels can be used to reduce speed fluctuations during mechanical operation. A rotating member having a proper moment of inertia and functioning as a storage and release kinetic energy is commonly used in machines, automobiles, bicycles, etc., and has a large rotational inertia of a wheel accumulator.
Flywheel function1 Store part of the energy of the engine's power stroke to overcome the resistance of other strokes and make the crankshaft rotate evenly.
2 Connect the engine to the vehicle drive system via a clutch mounted on the flywheel.
3 equipped with a ring gear engaged with the starter to facilitate engine starting.

At the power output of the crankshaft, that is, the gearbox and the side of the work equipment. The main function of the flywheel is to store the energy and inertia outside the engine's power stroke. The four-stroke engine only has the energy to inhale, compress, and exhaust the energy stored in the flywheel. The balance is corrected incorrectly. The balance of the engine is mainly based on the balance block on the shaft. The single-cylinder machine has a balance shaft.
The flywheel has a large moment of inertia. Since the work of each cylinder of the engine is discontinuous, the engine speed also changes. When the engine speed increases, the kinetic energy of the flywheel increases, and the energy is stored. When the engine speed decreases, the kinetic energy of the flywheel decreases, releasing energy. Flywheels can be used to reduce speed fluctuations during engine operation.

Installed at the rear end of the engine crankshaft, it has rotational inertia. Its function is to store the engine energy, overcome the resistance of other components, and make the crankshaft rotate evenly. Connect the engine and the car drive through the clutch mounted on the flywheel; The machine is engaged to facilitate engine starting. And it is the integration of crankshaft position sensing and vehicle speed sensing.
In the power stroke, the energy transmitted by the engine to the crankshaft, in addition to the external output, is partially absorbed by the flywheel, so that the rotational speed of the crankshaft does not rise much. In the three strokes of exhaust, intake and compression, the flywheel discharges its stored energy to compensate for the work consumed by these three strokes, so that the crankshaft speed is not reduced too much.

In addition, the flywheel has the following functions: the flywheel is the active part of the friction clutch; the flywheel rim is embedded with the flywheel ring gear for starting the engine; the top wheel is also engraved with the top dead center mark for calibration Ignition timing or injection timing, as well as adjusting valve clearance.
Flywheel moment of inertia calculation formula wheel flywheel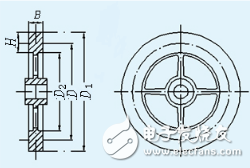
In the figure, the flywheel consists of a hub, a spoke and a rim. Since the other two parts have a small moment of inertia compared to the rim, they are generally omitted. After this simplification, the actual flywheel moment of inertia is slightly larger than the required moment of inertia. If the outer diameter of the flywheel is D1, the inner diameter of the rim is D2, and the mass of the rim is m, the moment of inertia of the rim is
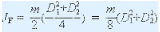
When the rim thickness H is not large, it can be approximated that the flywheel mass is concentrated on the circumference of its average diameter D, so
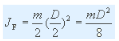
In the formula, m D2 is called the flywheel moment and its unit is kg·m2. Knowing the moment of inertia of the flywheel, you can find its flywheel moment. When the average diameter D of the rim is selected according to the installation space of the flywheel in the machine,
That is, the mass m of the flywheel can be calculated by the above formula. If the flywheel width is B (m), the rim thickness is H (m), the average diameter is D (m), and the material density is Ï (kg · m3), then
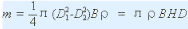
After D is selected and m is calculated by equation (10.28), the cross-sectional dimensions H and B of the flywheel can be obtained from equation (10.30) based on the material of the flywheel and the selected ratio H/B, for smaller flywheels. Usually, H/B≈2 is taken. For larger flywheels, H/B≈1.5 is usually taken.
It can be known from the formula (10.29) that when the flywheel inertia is constant, the larger the diameter of the selected flywheel, the smaller the mass. However, if the diameter is too large, it will increase manufacturing and transportation difficulties and occupy a large space. At the same time, the circumferential speed of the rim increases, which causes the flywheel to be ruptured by excessive centrifugal force. Therefore, the maximum peripheral speed of the flywheel should be verified to be less than the safety limit when determining the size of the flywheel.
Disc flywheelWhen the moment of inertia of the flywheel is not large, a disc-shaped flywheel of a simple shape can be used as shown.
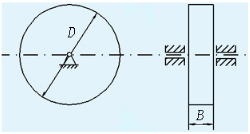
Let m, D and B be their mass, outer diameter and width respectively, then the moment of inertia of the whole flywheel is
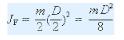
When the flywheel diameter D is selected according to the installation space, the flywheel mass m can be calculated from this formula. Another cause
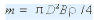
Therefore, according to the selected flywheel material, the width B of the flywheel can be obtained as
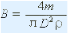
Insulated Power Cable,Bimetallic Crimp Lugs Cable,Pvc Copper Cable,Cable With Copper Tube Terminal
Taixing Longyi Terminals Co.,Ltd. , https://www.lycopperlugs.com