
Over the years, "autopilot" has become red. When we mention it, we will think of new cutting-edge technology companies such as Tesla and Google, as well as companies such as Ford, Chevrolet and Mercedes-Benz who are old-fashioned and closely follow the tide of the times. However, as everyone knows, in the field of automatic driving, there are still many unknown small companies hidden. These companies have been quietly heating up in the field of autonomous driving when big and powerful giants have made headlines on technology media. Oxbotica is one of them.
Although Oxbotica is not as famous as other giants, its autopilot technology can match it. Industry sources said: Oxbotica may be one of Google's few competitors. In 2015, Oxbotica was named one of the “10 most noteworthy companies†by The Wall Street Journal; in 2016, Oxbotica won the “2016 Software Automation Leader†award. So, what exactly does this company have to do? What makes so many industry professionals think about it?
Let ordinary cars learn to drive automaticallyOxbotica is a technology company bred by Oxford University and is dedicated to new software development. While major auto-pilot giants and auto makers are trying their best to create their own cool products, it is another way to turn ordinary cars into self-driving cars. The software developed by Oxbotica is called Selenium. It can obtain data information through vision system, laser scanner and radar system. Then it can use algorithms to determine the location of the target, understand the surrounding conditions and indicate the direction of movement. Therefore, the Selenium system can transform any car into a self-driving car.
Professor Paul Newman, co-founder of Oxford University and Oxbotica:
In addition to the general definition of private cars, equipment such as buses and engineering vehicles (such as excavators) can achieve automatic driving functions through "Selenium retrofit." In addition, the team does not only have to use software to control autonomous cars, but also warehouse robots, forklifts, and autonomous public transport.
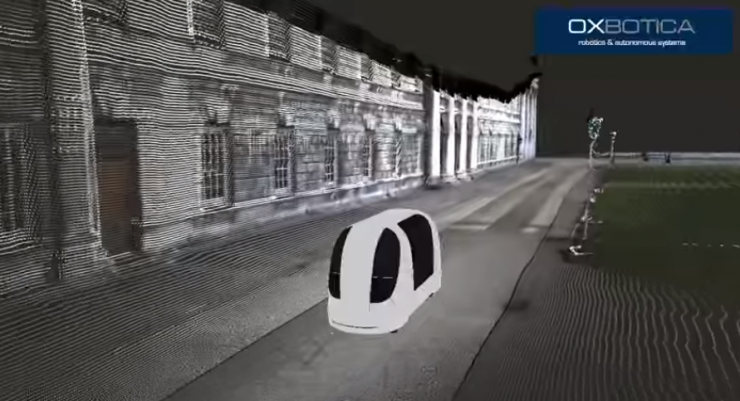
Selenium is a universal autopilot software system based on various on-board sensors and comprehensive data analysis. Each vehicle that is adapted to the Selenium system must undergo a “Seleniumization†transformation in advance. The transformation content mainly includes the installation and adaptation of relevant sensors and data analysis systems.
Unlike Tesla's self-driving cars, which have some autopilot capabilities from the outset, Selenium-equipped cars do not initially have the autopilot function, but rather have a learning ability. In the course of its journey, Selenium route data was obtained step by step to learn how to drive humans and continuously improve the ability to respond.
Oxbotica co-founder Ingmar Posner believes:
When we bought a driverless car and then started on the road, the car was ignorant at the very beginning. Only after driving for a certain period of time, the car can determine the location and understand the user's driving habits. The software will train the car sensing system and eventually realize the driverless driving.
Oxbotica software has two major functions: spatial orientation and perception of surrounding conditions. Central planners use two kinds of information planning directions. The car needs to use sensors to determine the location, sense the surrounding environment, and the functions of the car are different. We can choose to install different sensors. For example, a warehouse forklift can use a cheap camera, and a driverless car installs a variety of sensors.
In general, cars loaded with Selenium system use various sensors to obtain the surrounding environmental information. Then, combined with GPS map data, under the guidance of the user's driving behavior record, comprehensive analysis is performed through a set of unique algorithms of Oxbotica and then converted into operations. The behavior of the car achieves the purpose of automatic driving. In other words, Selenium system can get rid of the shackles of specific models and manufacturers, applied to a variety of models.
Selenium will soon conduct a live drive test. Currently, there are two projects using the software: one is the GATEway automatic driving public transport project in Greenwich, England, and the LUTZ Pathfinder pilotless capsule project is in Milton Keynes.

The scholastic team from Oxford
The reason why Oxbotica is so niubi is because there is a more daring team behind it. Oxbotica was born out of Oxford, so most of the team members come from this world famous school.

Oxbotica's founder and CEO is Graeme Smith. In addition to his Ph.D. from Oxford University, he has multiple identities: Ford's Director of Remote Technical Support, President of Wingcast Europe, a Ford General Cooperative Investment Company, Managing Director of IT Services Company SEI UK, and Vice President and Chief Operating Officer of Connexis LLC, a telematics service provider.
In addition, he is an expert in advanced vehicle control systems and connected car industries, and holds several patents in the application of vehicle systems for ACC (Adaptive Cruise System) and Pulsed Radar systems. At the same time, he has extensive experience in R&D, manufacturing, open source, and customer support.
For Selenium, Graeme Smith is confident:
Automated driving is already a trend, and Selenium we build will lead autopilot. For autonomous driving, it will be a revolutionary technology. We let people enjoy the pleasure of autonomous driving now, not the future.
Paul Newman, another team member , is a professor of information engineering at Oxford University and a member of EPSRC Leadership. In addition, he is also the head of the Mobile Robotics Group, which is dedicated to the development of machines, robots, automobiles, and navigation systems.
Today, the Oxbotica team has a total of nearly 130 members, and Selenium has been concentrating on their efforts over the years. Now, they are bravely marching forward.
Do more than just autopilot
In addition to developing software for vehicles, Oxbotica is also working on 3D map development and already has patents related to it. Maps developed by Oxbotica can quickly generate large-scale 3D real-time maps. The use of aggregating lasers results in lower production costs, but the accuracy is very high. Its application scope is very extensive. Apart from automotive positioning, zero infrastructure navigation, scene detection, and automatic driving, which are equal to the application of the automobile, it can also be used for urban planning, infrastructure management, and asset detection.

Today, Oxbotica owns about 40 exclusive intellectual property patents from Oxford University worldwide and attempts to commercialize these patents.
In addition, software developed by Oxbotica is not only used on vehicles, but also on mining equipment, agricultural equipment, ships, trains, and robots. Now, because of its very wide range of applications, there are also very many companies that work with it. Oxbotica currently seeks cooperation with car manufacturers, measurement companies, logistics companies, warehouse companies, civil engineering and construction companies, and even game companies.
Although the autopilot technology is good, for ordinary people, it seems as though there is still a long way to go for the benefits of autonomy. Oxbotica gave us a glimmer of hope: Autopilot seemed to be within easy reach. With its software installed, its own humble car could turn into a cool self-driving car. As the wheels of the times roll forward, Oxbotica takes the technology it is proud of and brings us to a better future.

Amd Gaming Pc,Gaming Computer,Gaming Pc I7,Pc Gamer
Shenzhen Innovative Cloud Computer Co., Ltd. , https://www.xcypc.com